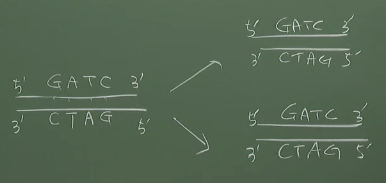http://www.ebsi.co.kr/ebs/lms/lmsx/retrieveSbjtDtl.ebs?sbjtId=S20180001029
17강 유전 물질(2)
================================================================================
Suppose following DNA
 ================================================================================
Cell division
Interphase
G1 (Gap1)
S (synthesis phase)
G2 (Gap2)
M phase (Mitotic phase)
Prophase
Prometaphase
Metaphase
Anaphase
Telophase
Cytokinesis
================================================================================
Cell division
Interphase
G1 (Gap1)
S (synthesis phase)
G2 (Gap2)
M phase (Mitotic phase)
Prophase
Prometaphase
Metaphase
Anaphase
Telophase
Cytokinesis
 books.google.co.kr/books?id=_fywAwAAQBAJ&printsec=frontcover&hl=ko#v=onepage&q&f=false
================================================================================
DNA replication during cell division, specifically S in Interphase
books.google.co.kr/books?id=_fywAwAAQBAJ&printsec=frontcover&hl=ko#v=onepage&q&f=false
================================================================================
DNA replication during cell division, specifically S in Interphase
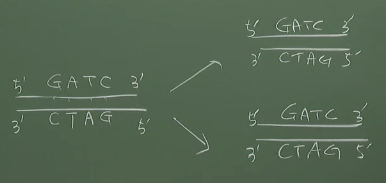 - anabolism: create polymer substance from small molecules
- ATP energy is needed
================================================================================
DNA replication way
semiconservative replication which is proved by Meselson and Stahl's experiment
- anabolism: create polymer substance from small molecules
- ATP energy is needed
================================================================================
DNA replication way
semiconservative replication which is proved by Meselson and Stahl's experiment
 ================================================================================
================================================================================
 * See 2 template strands
* See 2 template strands
 * Direction of 2 template strands
5' ----- 3'
3' ----- 5'
* Decouple the hydrogen bond by helicase
* Direction of decoupling
* Direction of 2 template strands
5' ----- 3'
3' ----- 5'
* Decouple the hydrogen bond by helicase
* Direction of decoupling
 * Now, you have 2 separated template strands
================================================================================
* DNA polymerase adds "corresponding base" to the base on the template strands
* Now, you have 2 separated template strands
================================================================================
* DNA polymerase adds "corresponding base" to the base on the template strands
 * Red: template strand
* Blue: newly added strand
* Red: template strand
* Blue: newly added strand
 ================================================================================
Mechanism of adding new strand
Existing nucleotide
================================================================================
Mechanism of adding new strand
Existing nucleotide
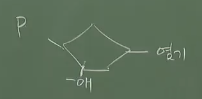 New nucleotide which has 3 Ps
New nucleotide which has 3 Ps
 This is called dNTP (deoxyribo-Nucleotide-Tri-Phospate)
2Ps are detached, and P and -OH have "covalent bond"
This is called dNTP (deoxyribo-Nucleotide-Tri-Phospate)
2Ps are detached, and P and -OH have "covalent bond"
 * Point: P is coupled only to -OH at C3
DNA polymerase can't replicate DNA without the prerequisite
The prerequisite is the small piece which supplies "-OH at C3"
The prerequisite is the RNA piece than DNA piece
The prerequisite is actually called "RNA primer" which is synthesized by "primase"
Then, DNA polymerase adds new nucleotides
https://youtu.be/TNKWgcFPHqw?t=69
* New nucleotide is added at "-OH at C3"
What does it mean?
New replicated strand is added in the direction of 5' $$$\rightarrow$$$ 3'
* See blue strand. 5' is located in the first position
* Point: P is coupled only to -OH at C3
DNA polymerase can't replicate DNA without the prerequisite
The prerequisite is the small piece which supplies "-OH at C3"
The prerequisite is the RNA piece than DNA piece
The prerequisite is actually called "RNA primer" which is synthesized by "primase"
Then, DNA polymerase adds new nucleotides
https://youtu.be/TNKWgcFPHqw?t=69
* New nucleotide is added at "-OH at C3"
What does it mean?
New replicated strand is added in the direction of 5' $$$\rightarrow$$$ 3'
* See blue strand. 5' is located in the first position
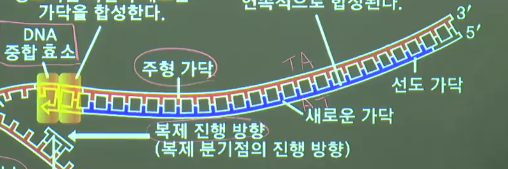
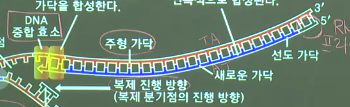 ================================================================================
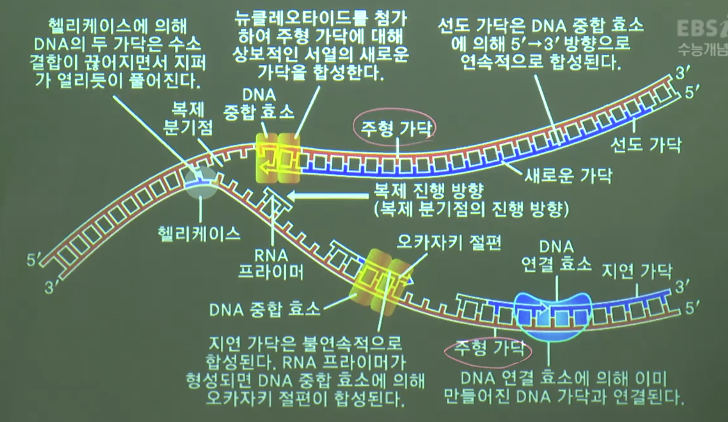
* DNA replication in this strand (leading strand) is fast
because replication direction is well fit
================================================================================
* DNA replication in this strand (leading strand) is fast
because replication direction is well fit
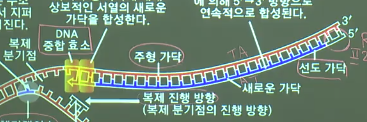 * DNA replication in this strand (lagging strand) is slow
because direction of replication is not fit
* Replicate small piece in the direction of 5' \rightarrow 3'
* DNA replication in this strand (lagging strand) is slow
because direction of replication is not fit
* Replicate small piece in the direction of 5' \rightarrow 3'
 * Replicate small piece in the direction of 5' \rightarrow 3'
* Replicate small piece in the direction of 5' \rightarrow 3'
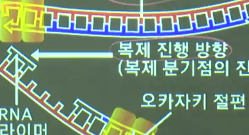
 * All replicated pieces are called Okazaki fragment
Okazaki fragment is connected by DNA ligase
================================================================================
After DNA replication, RNA primer is removed
Then, the place where RNA primer is removed becomes single strand which is unstable
So, single strand is decomposed, resulting in a bit shorter DNA
================================================================================
Generally, after 10 replications, cell becomes death
If people can protect the end (telomere) of DNA, lifespan becomes infinity
================================================================================
Cancer cell replicates continuously
The end of cancer cell is not decmposed
So, it will be good if people can apply the telomere-characteristic of cancer cell
to normal cell, to increase lifespan
================================================================================
* All replicated pieces are called Okazaki fragment
Okazaki fragment is connected by DNA ligase
================================================================================
After DNA replication, RNA primer is removed
Then, the place where RNA primer is removed becomes single strand which is unstable
So, single strand is decomposed, resulting in a bit shorter DNA
================================================================================
Generally, after 10 replications, cell becomes death
If people can protect the end (telomere) of DNA, lifespan becomes infinity
================================================================================
Cancer cell replicates continuously
The end of cancer cell is not decmposed
So, it will be good if people can apply the telomere-characteristic of cancer cell
to normal cell, to increase lifespan
================================================================================