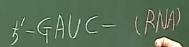http://www.ebsi.co.kr/ebs/lms/lmsx/retrieveSbjtDtl.ebs?sbjtId=S20180001029
================================================================================
mRNA,rRNA,tRNA=transcription(DNA)
if Eukaryota==True:
In nucleus:
mRNA,rRNA,tRNA=transcription(DNA)
================================================================================
enzymes_for_DNA_replication=[DNA_polymerase,helicase,primer,...]
DNA=DNA_replication(DNA,enzymes_for_DNA_replication)
================================================================================
enzymes_for_transcription=[RNA_polymerase,...]
mRNA,rRNA,tRNA=transcription(DNA,enzymes_for_transcription)
In transcription:
RNA_polymerase does the job of helicase,primer
================================================================================
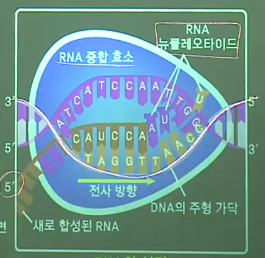
The detail of transcription
* Overview
 * RNA polymerase is attached to DAN, to start the transcription
Note that RNA polymerase is only attached to "promoter" location in the DNA
* RNA polymerase decouples DNA
* RNA polymerase is attached to DAN, to start the transcription
Note that RNA polymerase is only attached to "promoter" location in the DNA
* RNA polymerase decouples DNA
 * RNA polymerase creates RNA in the direction of 5' $$$\rightarrow$$$ 3'
Note that for transcription, only one DNA strand (3'5' one in this case) is used
* RNA polymerase creates RNA in the direction of 5' $$$\rightarrow$$$ 3'
Note that for transcription, only one DNA strand (3'5' one in this case) is used
 * You can see "lengthened RNA" and "recoupled DNA"
* You can see "lengthened RNA" and "recoupled DNA"
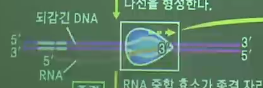 * When RNA polymerase arrives to the end point,
newly created RNA is separated from DNA, and RNA polymerase is also removed from the DNA
* When RNA polymerase arrives to the end point,
newly created RNA is separated from DNA, and RNA polymerase is also removed from the DNA
 ================================================================================
Even if RNA is created based on main-strand, but non-main-strand is still important
* Suppose following (non-main-strand, main-strand)
================================================================================
Even if RNA is created based on main-strand, but non-main-strand is still important
* Suppose following (non-main-strand, main-strand)
 * Imagine newly created RNA based on main-strand (3'5')
* Imagine newly created RNA based on main-strand (3'5')
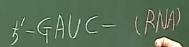 * Note that "non-main-strand" and "RNA" is same
if you replace T with U
* This is why non-main-strand is also called crypto-strand
================================================================================
* Note that "non-main-strand" and "RNA" is same
if you replace T with U
* This is why non-main-strand is also called crypto-strand
================================================================================
 * Note that these are "RNA nucleotides" which has "ribose" for pentan
* Note that these are "RNA nucleotides" which has "ribose" for pentan
 ================================================================================
Direction of trascription
* RNA grows from 5' to 3'
* RNA polymerase moves along DNA-main-strand from 3' to 5'
================================================================================
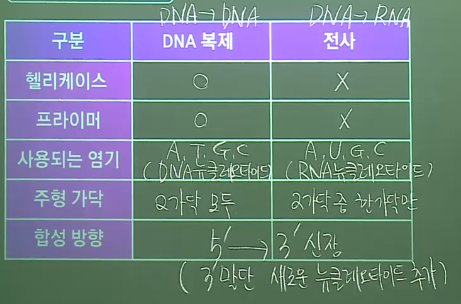
Comparison between DNA replication and RNA transcription
================================================================================
Direction of trascription
* RNA grows from 5' to 3'
* RNA polymerase moves along DNA-main-strand from 3' to 5'
================================================================================
Comparison between DNA replication and RNA transcription
 ================================================================================
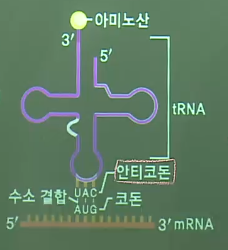
* tRNA's 3D model
================================================================================
* tRNA's 3D model
 * tRNA's 2D model
* tRNA's 2D model
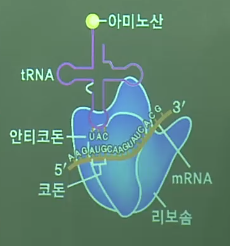
 * Combine tRNA with ribosome
* Combine tRNA with ribosome
 ================================================================================
* Ribosome: is the place where protein synthesis occurs
* Lysosome: it has hydrolase, so lysosome can do "digest in the cell"
================================================================================
================================================================================
* Ribosome: is the place where protein synthesis occurs
* Lysosome: it has hydrolase, so lysosome can do "digest in the cell"
================================================================================
 Ribosome = rRNA + protein
In the P in the nucleus of the cell:
rRNA=synthesize(DNA)
In the ribosome in the cytoplasm:
protein=synthesize(amino_acids)
move_to_nucleus(protein)
In the P in the nucleus of the cell:
sub_unit_of_ribosome,large_unit_of_ribosome=combine(rRNA,protein)
move_to_cytoplasm_via_nuclear pore(sub_unit_of_ribosome,large_unit_of_ribosome)
In the cytoplasm:
ribosome=combine(sub_unit_of_ribosome,large_unit_of_ribosome)
================================================================================
Ribosome = rRNA + protein
In the P in the nucleus of the cell:
rRNA=synthesize(DNA)
In the ribosome in the cytoplasm:
protein=synthesize(amino_acids)
move_to_nucleus(protein)
In the P in the nucleus of the cell:
sub_unit_of_ribosome,large_unit_of_ribosome=combine(rRNA,protein)
move_to_cytoplasm_via_nuclear pore(sub_unit_of_ribosome,large_unit_of_ribosome)
In the cytoplasm:
ribosome=combine(sub_unit_of_ribosome,large_unit_of_ribosome)
================================================================================
 Note that there is the place where mRNA is combined in the "sub unit of ribosome"
================================================================================
Note that there is the place where mRNA is combined in the "sub unit of ribosome"
================================================================================
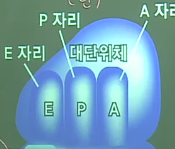 There are 3 places (A: amino acid,P: polypeptides,E:exit) in the large unit of ribosome
================================================================================
1.
There are 3 places (A: amino acid,P: polypeptides,E:exit) in the large unit of ribosome
================================================================================
1.
 combine(mRNA,sub_unit_of_ribosome)
There is no large_unit_of_ribosome in this stage
2.
combine(mRNA,sub_unit_of_ribosome)
There is no large_unit_of_ribosome in this stage
2.
 Codon: AUG
tRNA_with_methionine=get_tRNA_with_amino_acid(codon_AUG)
complementary_hydrogen_bond(codon_of_RNA,anti_codon_of_tRNA)
3
Codon: AUG
tRNA_with_methionine=get_tRNA_with_amino_acid(codon_AUG)
complementary_hydrogen_bond(codon_of_RNA,anti_codon_of_tRNA)
3
 .
large_unit_of_ribosome=get_large_unit_of_ribosome()
combine(sub_unit_of_ribosome,large_unit_of_ribosome)
4.
.
large_unit_of_ribosome=get_large_unit_of_ribosome()
combine(sub_unit_of_ribosome,large_unit_of_ribosome)
4.
 * second tRNA comes into A place and second tRNA is combined with mRNA
* second tRNA comes into A place and second tRNA is combined with mRNA
 5.
5.
 * Decomple Met and "first tRNS"
* Decomple Met and "first tRNS"
 * Perform "peptide bond"
* Perform "peptide bond"
 Enzyme for "peptide bond" is located in "large_unit_of_ribosome"
6.
Enzyme for "peptide bond" is located in "large_unit_of_ribosome"
6.
 move_ribosome(direction=[5',3'],step_size=one_codon_or_3_bases)
7.
move_ribosome(direction=[5',3'],step_size=one_codon_or_3_bases)
7.
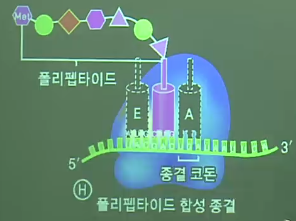 * Amino acid order
* Amino acid order
 * End codons: UAA,UAG,UGA
* End codons: UAA,UAG,UGA
 * Importantly note that
there is no tRNA which has anticodon which is corresponding to "ending codon"
* Importantly note that
there is no tRNA which has anticodon which is corresponding to "ending codon"