https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WzLsSCiOMTY
================================================================================
ChIP: [Ch]romatin [I]mmuno-[P]recipitation
================================================================================
Chromatin
- Status of DNA (which consists of chromosome) packed
Chromatin
- Complex structure with packed DNA, RNA, proteins, etc
DNA
- nucleosome -> chromatin -> chromosome
================================================================================
Our interest
- Interaction between "DNA" (which consists of chromatin) and "protein"
- You want to know "which sequence part of DNA" is coupled to "which protein"
================================================================================
ChIP-seq method
- You use "immuno" to precipitate the protein
- You sequence "brought DNA along with protein"
- You perform mapping "sequenced DNA" to reference genome
- Then, you can know the part where DNA and protein are coupled
================================================================================
ENCODE (Encyclopedia of DNA Elements) project
- After human genome project in 2003
- you could know that there are 20000 genes which code protein
- you could know that 20000 genes are 2% out of entire genome
- 50% is repetitive sequence
- And other 48%? Is it junk DNA?
- 20000 genes are rather small number of genes
- junk DNA controls axons?
- ENCODE project, 2003
- junk DNA has controling part?
- target cell is 100 billions number of cells
- because gene-expression is different in cell to cell
- Various experimental tools
- chromatin structure
- open chromatin (DNase-seq and FAIRE-seq)
- histone modifications and DNA-biding of over 100 transcription factor (ChIP-seq)
- RNA transcription (RNAseq and CAGE)
================================================================================
 ================================================================================
================================================================================
 nucleosome
================================================================================
nucleosome
================================================================================
 Open chromatin
Hypersensitive sites: places which can be cut easily by DNase enzyme
================================================================================
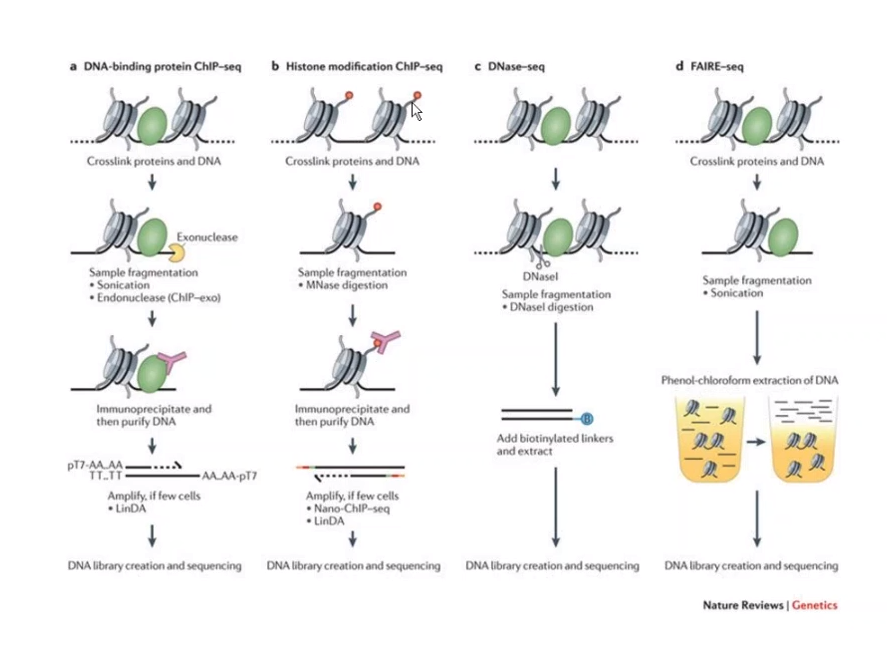
Overall step of ChIP-seq
Open chromatin
Hypersensitive sites: places which can be cut easily by DNase enzyme
================================================================================
Overall step of ChIP-seq
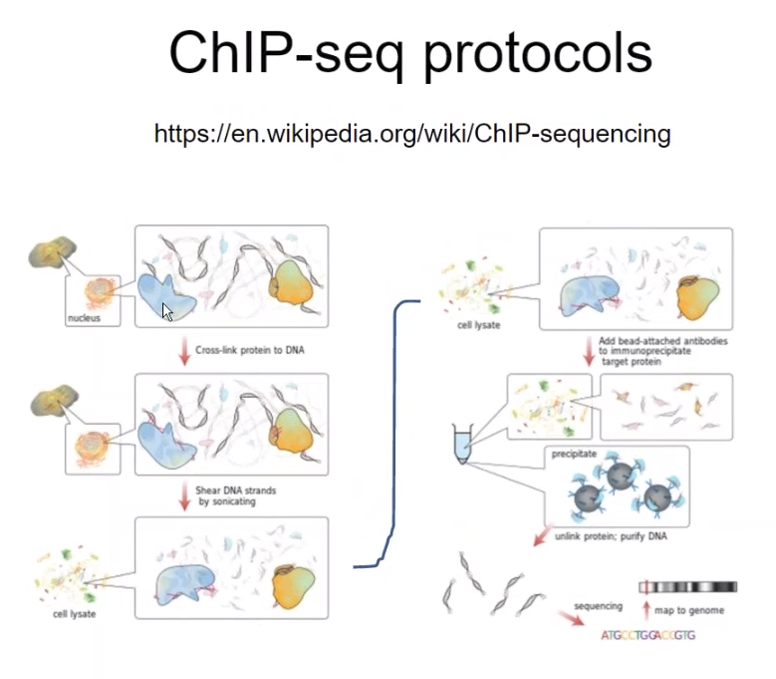 ================================================================================
================================================================================
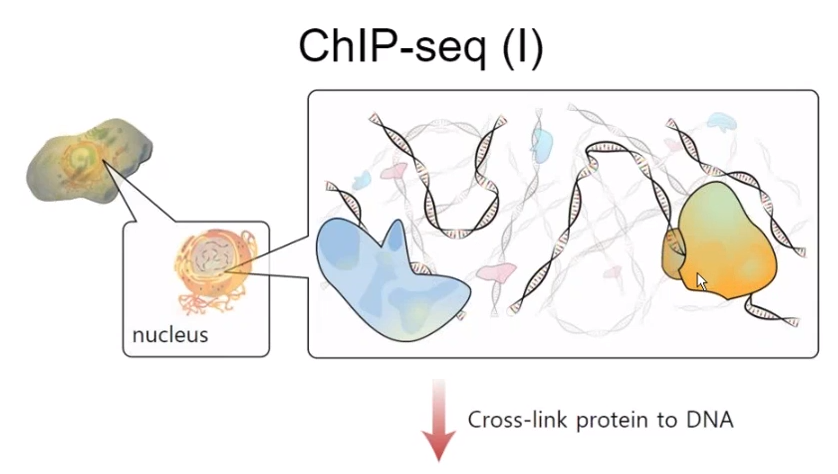 DNA is coupled to protein
================================================================================
DNA is coupled to protein
================================================================================
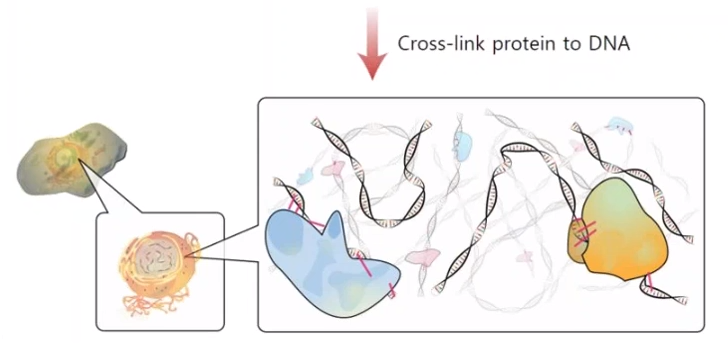 Cross-link between protein and DNA
- by using formaldehyde
- to create covalent bond between protein and DNA
- formaldehyde
- reaction between protein's amin group to formaldehyde
- it creates Schiff base
- covalent bond between DNA's amin group to protein's amin group
- it doesn't break other covalent bond, it creates additional covalent bond
- incubation in 70 cecius degree, induced covalent bond disappear
Cross-link between protein and DNA
- by using formaldehyde
- to create covalent bond between protein and DNA
- formaldehyde
- reaction between protein's amin group to formaldehyde
- it creates Schiff base
- covalent bond between DNA's amin group to protein's amin group
- it doesn't break other covalent bond, it creates additional covalent bond
- incubation in 70 cecius degree, induced covalent bond disappear
 ================================================================================
================================================================================
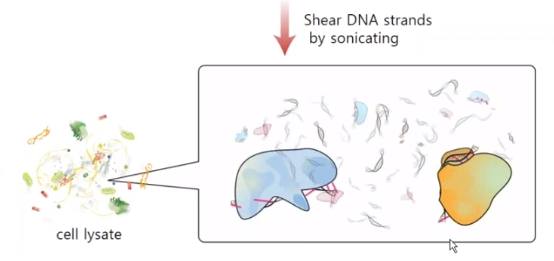
 Randomly cut DNAs by using sonication
================================================================================
Randomly cut DNAs by using sonication
================================================================================
 ================================================================================
================================================================================
 There are much various proteins which can couple with DNA
You should select one protein
And you perform "antigen-antibody reaction"
for example, "antigen-antibody reaction" for transcription factor FOXA3 (protein)
================================================================================
There are much various proteins which can couple with DNA
You should select one protein
And you perform "antigen-antibody reaction"
for example, "antigen-antibody reaction" for transcription factor FOXA3 (protein)
================================================================================
 ================================================================================
================================================================================
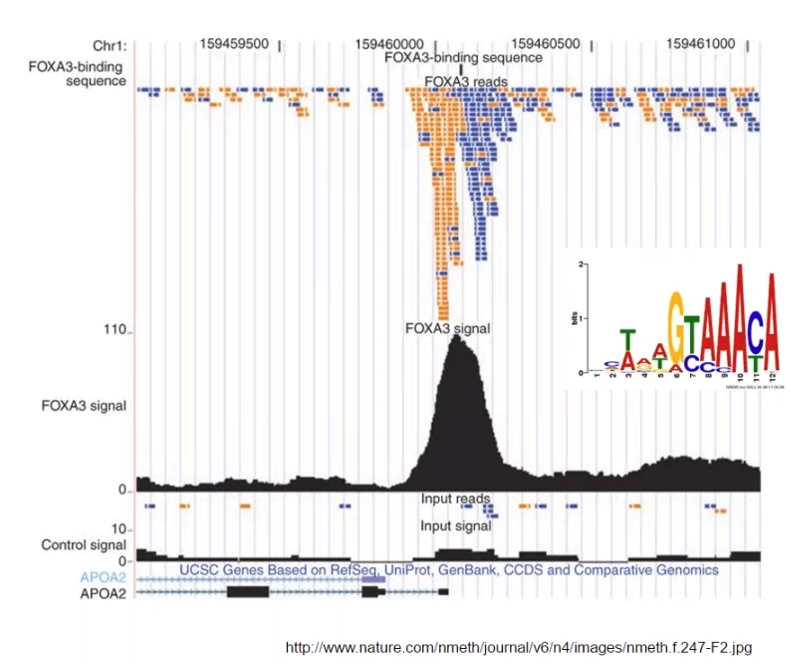 - Perform "antigen-antibody reaction" for transcription factor FOXA3 (protein) and antibody
- You get NGS reads
- You perform mapping NGS reads to reference genome
- You could know that NGS reads are much mapped to APOA2 gene part in 1st chromosome's reverse strand
================================================================================
Yellow: mapped result to forward strand
Blue: mapped result to reverse strand
================================================================================
- Perform "antigen-antibody reaction" for transcription factor FOXA3 (protein) and antibody
- You get NGS reads
- You perform mapping NGS reads to reference genome
- You could know that NGS reads are much mapped to APOA2 gene part in 1st chromosome's reverse strand
================================================================================
Yellow: mapped result to forward strand
Blue: mapped result to reverse strand
================================================================================
 FOXA3 binding site
================================================================================
FOXA3 binding site
================================================================================
 ================================================================================
================================================================================
 Left: various cell types
Top menu: various experiments
- Number in each square: number of dataset
================================================================================
Left: various cell types
Top menu: various experiments
- Number in each square: number of dataset
================================================================================
 Left: cell types
Top menu: antibody targets like histone protein
================================================================================
encodeproject.org
genome.ucsc.edu/ENCODE
================================================================================
Mutant: permanent change
================================================================================
Left: cell types
Top menu: antibody targets like histone protein
================================================================================
encodeproject.org
genome.ucsc.edu/ENCODE
================================================================================
Mutant: permanent change
================================================================================
 DNA methylation: Me is attached to C
On histone protein: acetylation, methylation, phosphorylation, ubiquitination
================================================================================
DNA methylation: Me is attached to C
On histone protein: acetylation, methylation, phosphorylation, ubiquitination
================================================================================
 CpG: Cytosine, Guanine
- CpG island: the place where CpG shows much more than normal
- Many gene's promoter has CpG island
- 5th location of Cytosine has high probability of methylation
- CpG's reverse complement is also CpG
- So, both strands (forward, reverse) have methylation
- DNA methylation is started by DNA methyltransferase (DNMT) enzyme
- When methylation occurs in gene's promoter's CpG island, gene expression is surpressed
- There are 2 hypothesises about how methylation works
- methylated CpG island in promoter can prevent the transcription factor to bind to promoter
- Proteins (which have methyl-CpG-binding domain (MBD)) recognize methylated CpG
and proteins are attached to methylated CpG
They bring "histone deacetylase (HDAC)" or "chromatin remodeling proteins"
And they convert histone structure (chromatin) into heterochromatin which is more tightly packing DNA
================================================================================
CpG: Cytosine, Guanine
- CpG island: the place where CpG shows much more than normal
- Many gene's promoter has CpG island
- 5th location of Cytosine has high probability of methylation
- CpG's reverse complement is also CpG
- So, both strands (forward, reverse) have methylation
- DNA methylation is started by DNA methyltransferase (DNMT) enzyme
- When methylation occurs in gene's promoter's CpG island, gene expression is surpressed
- There are 2 hypothesises about how methylation works
- methylated CpG island in promoter can prevent the transcription factor to bind to promoter
- Proteins (which have methyl-CpG-binding domain (MBD)) recognize methylated CpG
and proteins are attached to methylated CpG
They bring "histone deacetylase (HDAC)" or "chromatin remodeling proteins"
And they convert histone structure (chromatin) into heterochromatin which is more tightly packing DNA
================================================================================
 - Use MBD protein (which recognize methylated-CpG island)
- You can know methylated part by using sequencing
- Like ChIP-seq, you cut DNA by using sonication
- You induce precipitation by using antiboty against MBD
- You perform sequencing
- You perform mapping sequenced DNA to genome reference
================================================================================
- Use MBD protein (which recognize methylated-CpG island)
- You can know methylated part by using sequencing
- Like ChIP-seq, you cut DNA by using sonication
- You induce precipitation by using antiboty against MBD
- You perform sequencing
- You perform mapping sequenced DNA to genome reference
================================================================================
 N: negative
- CCDC8 gene has no methylation
T: tumor
- CCDC8 gene has much methylation
CCDC8 gene has CpG island
CCDC8 gene helps p53 which is cancer-surpressing gene
================================================================================
N: negative
- CCDC8 gene has no methylation
T: tumor
- CCDC8 gene has much methylation
CCDC8 gene has CpG island
CCDC8 gene helps p53 which is cancer-surpressing gene
================================================================================
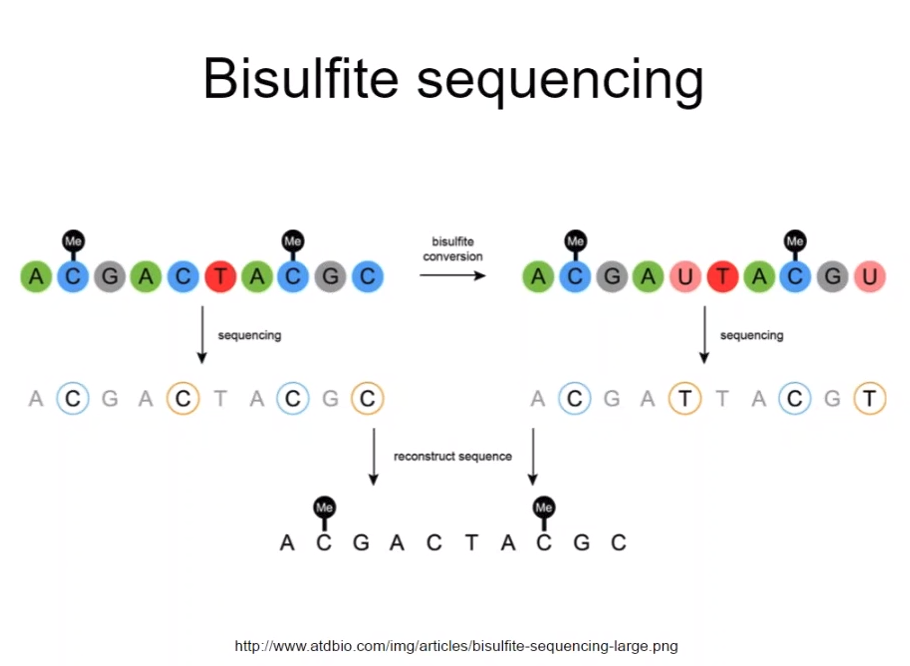 In the experiments using MBD protein,
you can't know sequenced DNA piece has methylation on which base
If you use bisulfite ($$$HSO_3^-$$$) on DNA,
Cytosine is converted Cytosinsulphonate -> Uracilsulphonate -> Uracil
On the other hand, 5-methylcytosine is not converted, but stay as it is
================================================================================
In the experiments using MBD protein,
you can't know sequenced DNA piece has methylation on which base
If you use bisulfite ($$$HSO_3^-$$$) on DNA,
Cytosine is converted Cytosinsulphonate -> Uracilsulphonate -> Uracil
On the other hand, 5-methylcytosine is not converted, but stay as it is
================================================================================
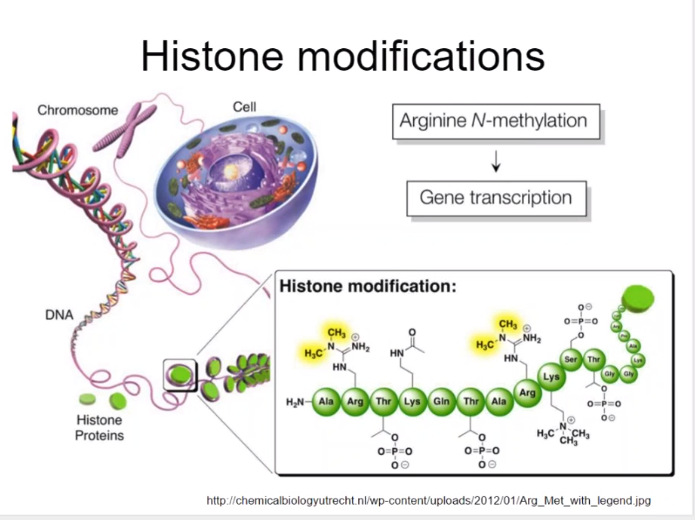 Histone protein:
4 kinds of protein
- H2A, H2B, H3, H4
- Entirely, 8 proteins (2*4)
- 8 proteins become the core of nucleosome
Histone protein's branches can take chemicals, resulting in adjust of gene expression or other biological steps
================================================================================
Histone protein:
4 kinds of protein
- H2A, H2B, H3, H4
- Entirely, 8 proteins (2*4)
- 8 proteins become the core of nucleosome
Histone protein's branches can take chemicals, resulting in adjust of gene expression or other biological steps
================================================================================
 High signal in RNA polymerase II (PolII) : places where transcriptions are performed actively
H3 protein's 4th, 36th lysine amino acid branch's trimethylation signal is high
27th lysine trimethylation is low
This histone status is called "histone code"
Combination of "histone code" controls gene expression and other biological step
================================================================================
High signal in RNA polymerase II (PolII) : places where transcriptions are performed actively
H3 protein's 4th, 36th lysine amino acid branch's trimethylation signal is high
27th lysine trimethylation is low
This histone status is called "histone code"
Combination of "histone code" controls gene expression and other biological step
================================================================================
 ================================================================================
================================================================================
 ================================================================================
================================================================================
 Almost 146 bases are wrapped around the histone
Almost 146 bases are wrapped around the histone

























