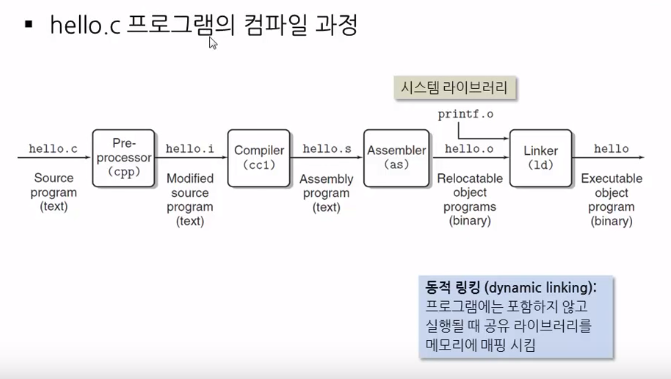
 Let's see steps of compiling hello.c file to create hello excutable file
Compile means to create an excutable file from a source file
But entire compilation has multiple steps which are managed
by multiple programs (Preprocessor(cpp), Compiler(cc1), Assembler(as), Linker(ld))
======================================================================
- Human writes c source file (hello.c)
- Preprocessor preprocesses hello.c,
creating pure C code (hello.1) which is still human readable
- Compiler creates "assembly program (text)" (hello.s)
which is text but no human readable like hexa codes
- Since "assembly program (text)" (hello.s) file is text file,
it should be converted into a binary file
which is managed by Assembler, creating hello.o (binary)
- Linker links system library files (like printf.o) and hello.o
to create one hello excutable binary file.
Or Linker can link multiple binary files (like hello1.o, hello2.o, ...)
when multiple source files (like hello1.c, hello2.c, ...) are given
from a developer to create one executable
Above step is called "static linking"
Dynaic linking means you don't include libraries into the executable file
but you map shared library files to memory in which executable file is loaded at runtime
======================================================================
Let's see how does excutable file which is created via a compilation-step look?
and when that excutable file is excuted,
how is that excutable file located in the memory?
This illustration is about the memory when excutable file is excuted
Let's see steps of compiling hello.c file to create hello excutable file
Compile means to create an excutable file from a source file
But entire compilation has multiple steps which are managed
by multiple programs (Preprocessor(cpp), Compiler(cc1), Assembler(as), Linker(ld))
======================================================================
- Human writes c source file (hello.c)
- Preprocessor preprocesses hello.c,
creating pure C code (hello.1) which is still human readable
- Compiler creates "assembly program (text)" (hello.s)
which is text but no human readable like hexa codes
- Since "assembly program (text)" (hello.s) file is text file,
it should be converted into a binary file
which is managed by Assembler, creating hello.o (binary)
- Linker links system library files (like printf.o) and hello.o
to create one hello excutable binary file.
Or Linker can link multiple binary files (like hello1.o, hello2.o, ...)
when multiple source files (like hello1.c, hello2.c, ...) are given
from a developer to create one executable
Above step is called "static linking"
Dynaic linking means you don't include libraries into the executable file
but you map shared library files to memory in which executable file is loaded at runtime
======================================================================
Let's see how does excutable file which is created via a compilation-step look?
and when that excutable file is excuted,
how is that excutable file located in the memory?
This illustration is about the memory when excutable file is excuted
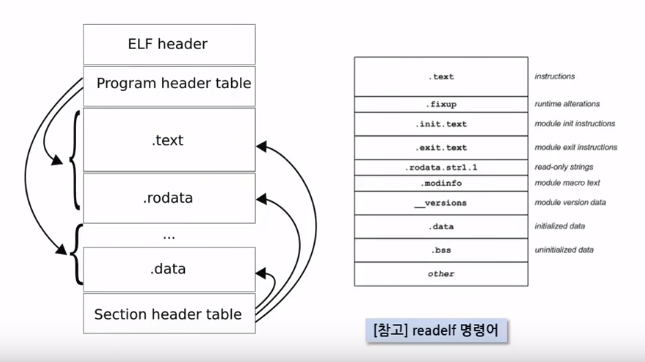
 This illustration describes the structure of the executable file (ELF)
This illustration describes the structure of the executable file (ELF)
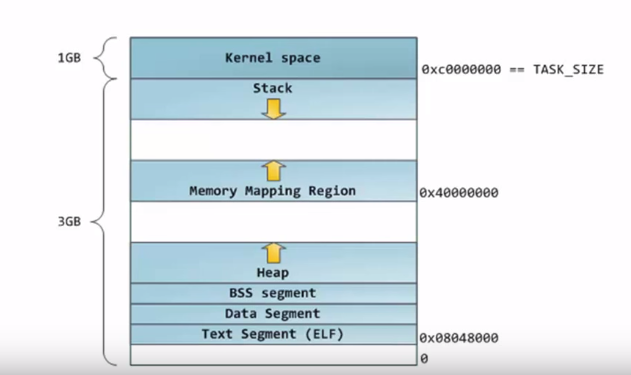
 When excutable file is excuted, it is located in the memory, which is called "process"
Excutable file itself (ELF) (the bottom one from first illustration) is small part out of process
You can see 1GB and 3GB
Those are memory size
First illustration describes the memory state when one program is excuted
which means that one program takes 4GB memory (but this is virtual memory not RAM)
======================================================================
This illustration describes the structure of the executable file (ELF)
When excutable file is excuted, it is located in the memory, which is called "process"
Excutable file itself (ELF) (the bottom one from first illustration) is small part out of process
You can see 1GB and 3GB
Those are memory size
First illustration describes the memory state when one program is excuted
which means that one program takes 4GB memory (but this is virtual memory not RAM)
======================================================================
This illustration describes the structure of the executable file (ELF)
 Linux has ELF format for excutable file structure
Windows has EXE format for excutable file structure
======================================================================
Linux has ELF format for excutable file structure
Windows has EXE format for excutable file structure
======================================================================



