https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aQn2t9FUs3U
================================================================================
Genetic algorithm
- 1975, John Holland
- Mimics evolution
- Global optimization search method
================================================================================
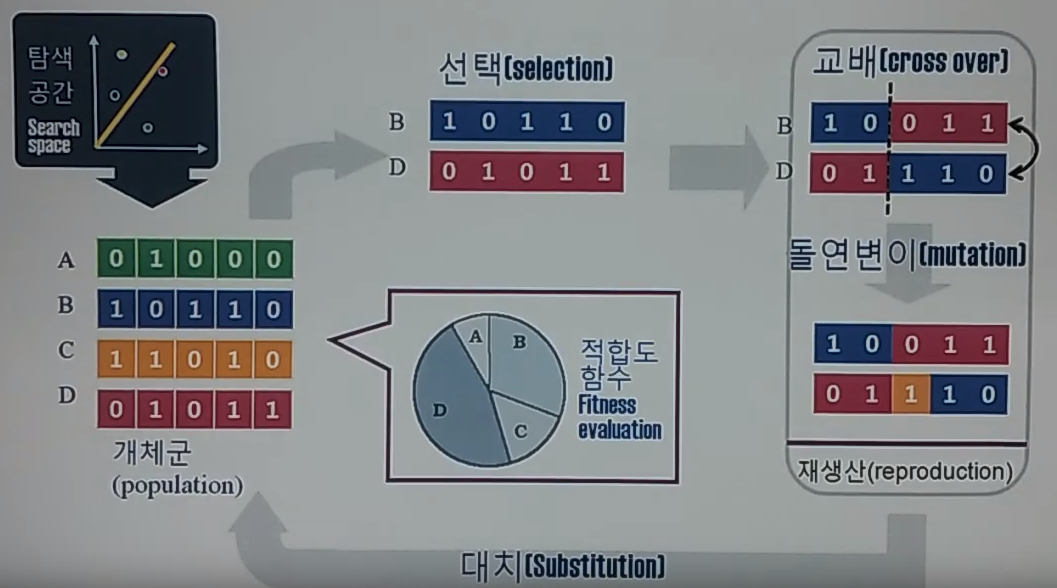 - You have "search space"
- You get "population"
- You select some of selections
- You perform "cross over"
- You get "mutation"
- You get "reproduction"
- You perform substitution into "population"
- You evaluate whether "population" satisfies the goal
by using "fitness evaluation"
- Iterate above steps
================================================================================
Components of genetic algorithm
Computational environment
- Population
- Set of input data
- Binary encoding, value encoding, tree encoding
- Genome
- Expresses genome of population
- Binary string, constant string, float string
- Generation
- Period of birth and death of genes
- Fitness function
- Evaluates how population (which you want to optimize) is fit to the given problem
Algorithm
- Selection
- Selects "chromosome"
- "chromosome" is used for "cross over"
- roulette wheel, ranking, tournament, preserving elite
- Cross over
- Mix gene of parent
- Simple cross over, 2 points cross over, uniform cross over, cycle cross over,
Ordered cross over, partial cross over, arithmetic cross over, heuristic cross over
- Mutation
- Select some of bits
- Change those bits
- 0.5-1.0% has mutation
- Substitution
- New gene replaces with old genes
- Good gene of parent is preserved
- Bad gene of parent is replaced with new gene
================================================================================
Use case
- Network
- Search optimal allocation in wireless network environment
- Produce system
- Optimal method via simulation in produce line
- NP-complete problem (P-NP problem)
- Hamilton route problem
- You have "search space"
- You get "population"
- You select some of selections
- You perform "cross over"
- You get "mutation"
- You get "reproduction"
- You perform substitution into "population"
- You evaluate whether "population" satisfies the goal
by using "fitness evaluation"
- Iterate above steps
================================================================================
Components of genetic algorithm
Computational environment
- Population
- Set of input data
- Binary encoding, value encoding, tree encoding
- Genome
- Expresses genome of population
- Binary string, constant string, float string
- Generation
- Period of birth and death of genes
- Fitness function
- Evaluates how population (which you want to optimize) is fit to the given problem
Algorithm
- Selection
- Selects "chromosome"
- "chromosome" is used for "cross over"
- roulette wheel, ranking, tournament, preserving elite
- Cross over
- Mix gene of parent
- Simple cross over, 2 points cross over, uniform cross over, cycle cross over,
Ordered cross over, partial cross over, arithmetic cross over, heuristic cross over
- Mutation
- Select some of bits
- Change those bits
- 0.5-1.0% has mutation
- Substitution
- New gene replaces with old genes
- Good gene of parent is preserved
- Bad gene of parent is replaced with new gene
================================================================================
Use case
- Network
- Search optimal allocation in wireless network environment
- Produce system
- Optimal method via simulation in produce line
- NP-complete problem (P-NP problem)
- Hamilton route problem
