================================================================================
Mean vector
$$$E[X] \\
= [E[X_1], E[X_2], \cdots, E[X_N]]^T \\
= [\mu_1,\mu_2,\cdots,\mu_N]^T \\
= \pmb{\mu}$$$
* $$$E[X]$$$: Mean vector
================================================================================
Covariance matrix:
(1) represents relationship between features of each dimention as covariance (off-diagonal regions)
(2) represents variance of features in each dimenstion as variance (diagonal axis positions)
================================================================================
$$$COV[X] \\
= \Sigma \\
= E[(X-\mu)(X-\mu)^T] \\
= \begin{bmatrix}
E[(x_1-\mu_1)(x_1-\mu_1)^T]&&\cdots&&E[(x_1-\mu_1)(x_N-\mu_N)^T]\\
\cdots&&\cdots&&\cdots\\
E[(x_N-\mu_N)(x_1-\mu_1)^T]&&\cdots&&E[(x_N-\mu_N)(x_N-\mu_N)^T]\\
\end{bmatrix} \\
= \begin{bmatrix}
\sigma_1^2&&\cdots&&C_{IN}\\
\cdots&&\cdots&&\cdots\\
C_{IN}&&\cdots&&\sigma_{N}^2\\
\end{bmatrix}$$$
* $$$C_{IN}$$$: covariance between ith and Nth
================================================================================
Characteristics of covariance
- $$$x_i$$$, $$$x_k$$$ increase together, covariance value $$$c_{ik}>0$$$
- $$$x_k$$$ increases, $$$x_i$$$ decreases, covariance value $$$c_{ik}\lt 0$$$
- $$$x_i$$$ and $$$x_k$$$ are uncorrelated, covariance value $$$c_{ik} = 0$$$
- $$$|c_{ik}| \lt \sigma_i\times \sigma_k$$$, $$$\sigma_i$$$ is std of $$$x_i$$$
- $$$c_{ii} = \sigma_i^2 = VAR(x_i)$$$
================================================================================
* $$$\rho_{ik}$$$: correlation coefficient
(1) $$$-1\le \rho_{ik}\le 1$$$
(2) $$$\rho_{ik}=-1$$$: highest negative correlation
(2) $$$\rho_{ik}=1$$$: highest positive correlation
* $$$c_{ik} = \rho_{ik} \sigma_i\sigma_k$$$
* $$$\rho_{ik}=\dfrac{c_{ik}}{\sigma_i\sigma_k}$$$
================================================================================
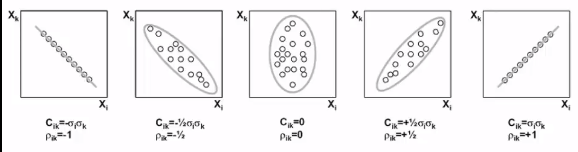 * Each circle: each sample data
================================================================================
(1) $$$X_1$$$ decreases and $$$X_k$$$ increases
* $$$c_{ik}=-\sigma_i \sigma_k$$$
* $$$\rho_{ik}=-1$$$
(2) $$$X_1$$$ decreases and $$$X_k$$$ increases
* $$$c_{ik}=-\frac{1}{2} \sigma_i \sigma_k$$$
* $$$\rho_{ik}=-\frac{1}{2}$$$
(3) $$$X_1$$$ and $$$X_k$$$ are uncorrelated
* $$$c_{ik}=0$$$
* $$$\rho_{ik}=0$$$
* Each circle: each sample data
================================================================================
(1) $$$X_1$$$ decreases and $$$X_k$$$ increases
* $$$c_{ik}=-\sigma_i \sigma_k$$$
* $$$\rho_{ik}=-1$$$
(2) $$$X_1$$$ decreases and $$$X_k$$$ increases
* $$$c_{ik}=-\frac{1}{2} \sigma_i \sigma_k$$$
* $$$\rho_{ik}=-\frac{1}{2}$$$
(3) $$$X_1$$$ and $$$X_k$$$ are uncorrelated
* $$$c_{ik}=0$$$
* $$$\rho_{ik}=0$$$
