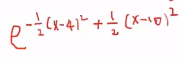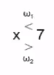Key points:
- Statistical methods
- Likelihood ratio test
- Maximum likelihood estimation
- Likelihood
================================================================================
pattern=statistical_decision_theory(data)
================================================================================
decision_function,decision_region,decision_boundary=likelihood_ratio_test()
================================================================================
estimated_prob_density_function=maximum_likelihood_estimation(data)
================================================================================
Likelihood: how much similar?
LRT: test "similarity" by using "ratio"
================================================================================
* LRT:
* You suppose you know probability density function of data
* Now, you want to classify that data based on probability density function
================================================================================
* Classification example
* You have data composed of weight values and height values
* By using that data, create classifier model,
* and classify given feature vector x composed of height and weight
================================================================================
* Method1
* Code
posterior_prob_val_of_class1=posterior_prob_of_class1(feature_vec1)
posterior_prob_val_of_class2=posterior_prob_of_class2(feature_vec1)
posterior_prob_list=[posterior_prob_val_of_class1,posterior_prob_val_of_class2]
idx_of_max=max(posterior_prob_list)
selected_class=posterior_prob_list[idx_of_max]
================================================================================
* Method1
* Math
Posterior prob = prior prob $$$\times$$$ likelihood
$$$P(\omega_i|x) = P(\omega_i) \times P(x|\omega_i)$$$
* $$$P(\omega_i) \approx \frac{N_i}{N}$$$
$$$N$$$: number of samples
$$$N_i$$$: number of samples resided in class $$$\omega_i$$$
If $$$N$$$ is enough bigger, $$$\frac{N_i}{N}$$$ becomes more similar to $$$P(\omega_i)$$$
* If P(\omega_1|x) > P(\omega_2|x), choose class $$$\omega_1$$$
else, choose class $$$\omega_2$$$
* Math notation for above sentence
 * Red square is likelihood ratio
* You can classify class of feature vector
based on likelihood ratio and prior probability ratio
================================================================================
* Example
* 2 classes: $$$\omega_1$$$, $$$\omega_2$$$
* probability density function
1. Probability distribution of $$$\omega_1$$$ occuring
$$$P(x|\omega_1)= \frac{1}{\sqrt{2\pi}} e^{\frac{1}{2} (x-4)^2}$$$
$$$N(\mu=4,\sigma=1)$$$
2. Probability distribution of $$$\omega_2$$$ occuring
$$$P(x|\omega_2)= \frac{1}{\sqrt{2\pi}} e^{\frac{1}{2} (x-10)^2}$$$
$$$N(\mu=10,\sigma=1)$$$
* Red square is likelihood ratio
* You can classify class of feature vector
based on likelihood ratio and prior probability ratio
================================================================================
* Example
* 2 classes: $$$\omega_1$$$, $$$\omega_2$$$
* probability density function
1. Probability distribution of $$$\omega_1$$$ occuring
$$$P(x|\omega_1)= \frac{1}{\sqrt{2\pi}} e^{\frac{1}{2} (x-4)^2}$$$
$$$N(\mu=4,\sigma=1)$$$
2. Probability distribution of $$$\omega_2$$$ occuring
$$$P(x|\omega_2)= \frac{1}{\sqrt{2\pi}} e^{\frac{1}{2} (x-10)^2}$$$
$$$N(\mu=10,\sigma=1)$$$
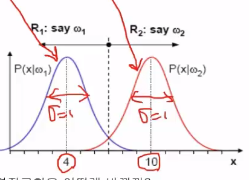 * Supposed condition: same prior probability
$$$P(\omega_1)=P(\omega_2)$$$
================================================================================
* Supposed condition: same prior probability
$$$P(\omega_1)=P(\omega_2)$$$
================================================================================
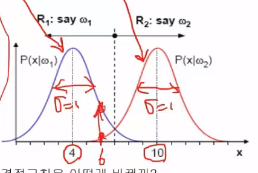 * When you're given data of 6
* its class should be classified to $$$\omega_1$$$
================================================================================
* When you're given data of 6
* its class should be classified to $$$\omega_1$$$
================================================================================
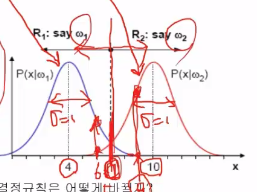 * Decision boundary: center vertical line, x=7
* It's "finding a classification boundary via LRT"
================================================================================
* Decision boundary: center vertical line, x=7
* It's "finding a classification boundary via LRT"
================================================================================
 * Since you had supposed that $$$P(\omega_1)=P(\omega_2)$$$
* $$$\dfrac{\text{likelihood of class\;}$$$\omega_1$$$}{\text{likelihood of class\;}$$$\omega_2$$$}$$$
================================================================================
* Above equation becomes simplified into
* Since you had supposed that $$$P(\omega_1)=P(\omega_2)$$$
* $$$\dfrac{\text{likelihood of class\;}$$$\omega_1$$$}{\text{likelihood of class\;}$$$\omega_2$$$}$$$
================================================================================
* Above equation becomes simplified into
 ================================================================================
* Left fraction term can be simplified to
================================================================================
* Left fraction term can be simplified to
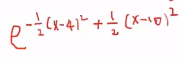 ================================================================================
* You apply log
================================================================================
* You apply log
 ================================================================================
* Finally, you get
================================================================================
* Finally, you get
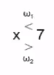 ================================================================================
================================================================================