================================================================================
* k-NNR is not ultimately precise
* It's hard to say it's actual PDF
* Usage of k-NNR
- It can be used with Bayes classifier
- It can induce simple approximation from Bayes classifier
================================================================================
* N number of samples
* multiple classes
* $$$N_{i}$$$: sample from class $$$\omega_i$$$
* Your goal: classify $$$x_{u}$$$ into $$$\omega_{1}$$$ or $$$\omega_{2}$$$
* Dimension of feature: N
* Space for N dimension: hyper sphere
* Suppose specific volumn V contains k number of samples
================================================================================
 * Red dots: samples
* Green dots: unknown data
* Red dots: samples
* Green dots: unknown data
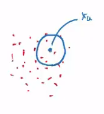 * Suppose volume V
* Count involved samples
================================================================================
* Suppose volume V
* Count involved samples
================================================================================
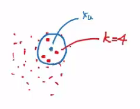 * k=4
================================================================================
* k=4
================================================================================
 * Suppose 2 samples (2 green dots) are from ith class $$$\omega_i$$$
* $$$k_i=2$$$
================================================================================
* Approximated likelihood via k-NNR
$$$P(x|\omega_i)=\frac{k_i}{N_iV}$$$
* Approximated unconditional density $$$P(x)= \frac{k}{NV}$$$
* Approximated prior probability $$$P(\omega_i)=\frac{N_i}{N}$$$
================================================================================
* Conclusion
* Your ultimate goal is to calculate posterior probability $$$P(\omega|x)$$$
which can be calculated via Bayes theorem
* $$$P(\omega|x)$$$ can be approximated via k-NNR
$$$P(\omega|x)
= \dfrac{P(x|\omega_i)P(\omega_i)}{P(x)} \\
= \dfrac{\frac{k_i}{N_iV} \frac{N_i}{N} }{\frac{k}{NV}} \\
= \dfrac{k_i}{k}$$$
================================================================================
* Example
* One V contains 6 entire samples in that region
* 2 samples are from class $$$\omega_i$$$
* $$$P(\omega|x) = \frac{2}{6}$$$
================================================================================
* Summary
* You are given unknow data
* Set contant k, suppose k=5
* Draw volume
* Suppose 2 samples (2 green dots) are from ith class $$$\omega_i$$$
* $$$k_i=2$$$
================================================================================
* Approximated likelihood via k-NNR
$$$P(x|\omega_i)=\frac{k_i}{N_iV}$$$
* Approximated unconditional density $$$P(x)= \frac{k}{NV}$$$
* Approximated prior probability $$$P(\omega_i)=\frac{N_i}{N}$$$
================================================================================
* Conclusion
* Your ultimate goal is to calculate posterior probability $$$P(\omega|x)$$$
which can be calculated via Bayes theorem
* $$$P(\omega|x)$$$ can be approximated via k-NNR
$$$P(\omega|x)
= \dfrac{P(x|\omega_i)P(\omega_i)}{P(x)} \\
= \dfrac{\frac{k_i}{N_iV} \frac{N_i}{N} }{\frac{k}{NV}} \\
= \dfrac{k_i}{k}$$$
================================================================================
* Example
* One V contains 6 entire samples in that region
* 2 samples are from class $$$\omega_i$$$
* $$$P(\omega|x) = \frac{2}{6}$$$
================================================================================
* Summary
* You are given unknow data
* Set contant k, suppose k=5
* Draw volume
 * Calculate each posterior probability value
$$$\frac{4}{5}, \frac{1}{5}, \frac{0}{5}$$$
* Calculate each posterior probability value
$$$\frac{4}{5}, \frac{1}{5}, \frac{0}{5}$$$
 * Classify unknown data into class $$$\omega_1$$$
* Even if you used k-NNR method, result is same with the case
where you use Bayes classifier
================================================================================
* Classify unknown data into class $$$\omega_1$$$
* Even if you used k-NNR method, result is same with the case
where you use Bayes classifier
================================================================================
 ================================================================================
================================================================================
 * All same except for k
* Too large k, or bad k result in bad result
* All same except for k
* Too large k, or bad k result in bad result







