================================================================================
Researchers was trying to induce a linear algebric way,
which could satisfy following conditions:
- preserve variance of high dimenstion feature vector data
- reduce dimension of feature vector
Researchers could find the PCA
================================================================================
 * 2D feature vector data
* feat_vec1=[height=170,weight=60]
* Mean of data is located in center (red dot)
================================================================================
* Variance can be described by "covariance matrix $$$\Sigma$$$"
$$$\Sigma = \begin{bmatrix} \sigma_1^2&&c_{12}\\c_{12}&&\sigma_2^2 \end{bmatrix}$$$
* 2D feature vector data
* feat_vec1=[height=170,weight=60]
* Mean of data is located in center (red dot)
================================================================================
* Variance can be described by "covariance matrix $$$\Sigma$$$"
$$$\Sigma = \begin{bmatrix} \sigma_1^2&&c_{12}\\c_{12}&&\sigma_2^2 \end{bmatrix}$$$
 ================================================================================
* Covariance matrix is square matrix
* Square matrix has eigenvector and eigenvalue
$$$\Sigma = \begin{bmatrix} u_1&&u_2 \end{bmatrix} \times
\begin{bmatrix} \lambda_1&&0\\0&&\lambda_1 \end{bmatrix} \times
\begin{bmatrix} u_1\\u_2 \end{bmatrix}$$$
* $$$\begin{bmatrix} u_1&&u_2 \end{bmatrix}$$$: eigenvector of $$$\Sigma$$$
* $$$\begin{bmatrix} \lambda_1&&0\\0&&\lambda_1 \end{bmatrix}$$$: eigenvalues (in matrix) of $$$\Sigma$$$
================================================================================
================================================================================
* Covariance matrix is square matrix
* Square matrix has eigenvector and eigenvalue
$$$\Sigma = \begin{bmatrix} u_1&&u_2 \end{bmatrix} \times
\begin{bmatrix} \lambda_1&&0\\0&&\lambda_1 \end{bmatrix} \times
\begin{bmatrix} u_1\\u_2 \end{bmatrix}$$$
* $$$\begin{bmatrix} u_1&&u_2 \end{bmatrix}$$$: eigenvector of $$$\Sigma$$$
* $$$\begin{bmatrix} \lambda_1&&0\\0&&\lambda_1 \end{bmatrix}$$$: eigenvalues (in matrix) of $$$\Sigma$$$
================================================================================
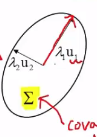 * Direction of axis is eigenvector $$$\begin{bmatrix} u_1&&u_2 \end{bmatrix}$$$
* Length of axis is eigenvalue
* one eigenvalue > the other eigenvalue
================================================================================
* Direction of axis is eigenvector $$$\begin{bmatrix} u_1&&u_2 \end{bmatrix}$$$
* Length of axis is eigenvalue
* one eigenvalue > the other eigenvalue
================================================================================
 ================================================================================
================================================================================
 * Reduce 2D feature vector into 1D feature vector
* Variance of 2D feature vector data is preserved
* 2D feature vector data is projected onto axis $$$u_1$$$
================================================================================
* Reduce 2D feature vector into 1D feature vector
* Variance of 2D feature vector data is preserved
* 2D feature vector data is projected onto axis $$$u_1$$$
================================================================================
 * When you use axis $$$u_2$$$
* variance of 2D feature vector data is not preserved
================================================================================
* Steps of dimensionality reduction using PCA
- Find covariance matrix of feature vector data
- Find eigenvalue and eigenvector of covariance matrix
- Find largest eigenvalue to find a direction of principal components
- Project feature vector data onto the found axis
=================================================================
* 3D feature vector data can be represented by 3 axes
* 10D feature vector data into 4D feature vector data means reducing number of axes from 10 to 4
================================================================================
* N number of D dimension feature vector data $$$x_n$$$
* Find (D,D) covariance matrix $$$\Sigma$$$
* $$$\mu=\dfrac{1}{N} \sum\limits_{n=1}^{N} x_n$$$
* $$$\Sigma=\dfrac{1}{N-1} \sum\limits_{n=1}^{N} (x_n-\mu)(x_n-\mu)^T$$$
* Eigenvalue analysis
$$$\Sigma = U\Lambda U^T = \begin{bmatrix} u_1&&u_2&&\cdots&&u_D \end{bmatrix}
\begin{bmatrix} \lambda_1&&0&&0\\0&&\ddots&&0\\0&&0&&\lambda_D \end{bmatrix}
\begin{bmatrix} u_1\\u_2\\\vdots\\u_D \end{bmatrix}$$$
* From D number of eigenvalues, select M number of largest eigenvalues $$$\{\lambda_1,\lambda_2,\cdots,\lambda_M\}$$$
* Create transformation matrix $$$W$$$ by using $$$u$$$ and $$$\lambda$$$
* Feature vector into lower dimension
$$$y=W^Tx$$$
* When you use axis $$$u_2$$$
* variance of 2D feature vector data is not preserved
================================================================================
* Steps of dimensionality reduction using PCA
- Find covariance matrix of feature vector data
- Find eigenvalue and eigenvector of covariance matrix
- Find largest eigenvalue to find a direction of principal components
- Project feature vector data onto the found axis
=================================================================
* 3D feature vector data can be represented by 3 axes
* 10D feature vector data into 4D feature vector data means reducing number of axes from 10 to 4
================================================================================
* N number of D dimension feature vector data $$$x_n$$$
* Find (D,D) covariance matrix $$$\Sigma$$$
* $$$\mu=\dfrac{1}{N} \sum\limits_{n=1}^{N} x_n$$$
* $$$\Sigma=\dfrac{1}{N-1} \sum\limits_{n=1}^{N} (x_n-\mu)(x_n-\mu)^T$$$
* Eigenvalue analysis
$$$\Sigma = U\Lambda U^T = \begin{bmatrix} u_1&&u_2&&\cdots&&u_D \end{bmatrix}
\begin{bmatrix} \lambda_1&&0&&0\\0&&\ddots&&0\\0&&0&&\lambda_D \end{bmatrix}
\begin{bmatrix} u_1\\u_2\\\vdots\\u_D \end{bmatrix}$$$
* From D number of eigenvalues, select M number of largest eigenvalues $$$\{\lambda_1,\lambda_2,\cdots,\lambda_M\}$$$
* Create transformation matrix $$$W$$$ by using $$$u$$$ and $$$\lambda$$$
* Feature vector into lower dimension
$$$y=W^Tx$$$





