009-001. GAN1
# @
# You will implement Generative Adversarial Network(GAN),
# which is unsupervised learning
# https://arxiv.org/abs/1406.2661
# @
import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
mnist=input_data.read_data_sets("/media/young/5e7be152-8ed5-483d-a8e8-b3fecfa221dc/programming materials/mnist/data/",one_hot=True)
# @
# You configure options
total_epoch=10
batch_size=100
learning_rate=0.0002
# They're options which consist of neural network layers
n_hidden=256
n_input=28*28
# This is sie of noise,
# which will be passed into constructor as argument
n_noise=128
# @
# You will build neural network model
# GAN doesn't use y label like autoencoder,
# because they're unsupervised learning
X=tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,n_input])
# You will use noise Z as input
Z=tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,n_noise])
# They're parameters which are used in constructor of neural network
G_W1=tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_noise,n_hidden],stddev=0.01))
G_b1=tf.Variable(tf.zeros([n_hidden]))
G_W2=tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_hidden,n_input],stddev=0.01))
G_b2=tf.Variable(tf.zeros([n_input]))
# They're parameters which are used in classifier neural network
D_W1=tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_input,n_hidden],stddev=0.01))
D_b1=tf.Variable(tf.zeros([n_hidden]))
# Last value of claasifier is one scalar value,
# which represents how much near to true
D_W2=tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_hidden,1],stddev=0.01))
D_b2=tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1]))
# This method builds generator of neural network
def generator(noise_z):
hidden=tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(noise_z,G_W1)+G_b1)
output=tf.nn.sigmoid(tf.matmul(hidden,G_W2)+G_b2)
return output
# This method build classifier of neural network
def discriminator(inputs):
hidden=tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(inputs,D_W1)+D_b1)
output=tf.nn.sigmoid(tf.matmul(hidden,D_W2)+D_b2)
return output
# This method creates random noise z
def get_noise(batch_size,n_noise):
return np.random.normal(size=(batch_size,n_noise))
# You create random image by using noise
G=generator(Z)
# You find value which decides if created image is true or not
D_gene=discriminator(G)
# You find true value,
# which outputs true decision value with true image
D_real=discriminator(X)
# According to paper,
# optimization of GAN model is to maximize loss_G and loss_D
# But, since loss_D and loss_G have correlation,
# you won't see both losses increase together
# loss_D and loss_G have competitive correlation
# loss_D to be increased, loss_G should be decreased
# According to pater, to maximize loss_D, you should minimize D_gene
# You will train model to have tf.log(D_real) as maximumal value,
# when you input true image into claasifier
# You will train model to have tf.log(1-D_gene) as maximumal value,
# when you input fake image into claasifier
# This means you will train model to decide fake image is not true
loss_D=tf.reduce_mean(tf.log(D_real)+tf.log(1-D_gene))
# To maximize loss_G, you should maximize D_gene
# This means you will generator neural network to decide true image,
# when you input fake image
# In paper, it uses same formular for loss_D to find minimizing generator
# But, since what you will do is to maximize D_gene,
# you can use following code
loss_G=tf.reduce_mean(tf.log(D_gene))
# You optimize by using parameters which are used in decision neural network,
# when you find loss_D
D_var_list=[D_W1,D_b1,D_W2,D_b2]
# You optimize by using parameters which are used in generator neural network,
# when you find loss_G
G_var_list=[G_W1,G_b1,G_W2,G_b2]
# You should maximize loss
# But since we will use minimize function,
# we will append - on loss_D and loss_G to maximize them
train_D=tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate)\
.minimize(-loss_D,var_list=D_var_list)
train_G=tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate)\
.minimize(-loss_G,var_list=G_var_list)
# @
# You will train neural network
sess=tf.Session()
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
total_batch=int(mnist.train.num_examples/batch_size)
loss_val_D,loss_val_G=0,0
for epoch in range(total_epoch):
for i in range(total_batch):
batch_xs,batch_ys=mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size)
noise=get_noise(batch_size,n_noise)
# You train decision neural network
_,loss_val_D=sess.run([train_D,loss_D],feed_dict={X: batch_xs,Z: noise})
# You train generator neural network
_,loss_val_G=sess.run([train_G,loss_G],feed_dict={Z: noise})
print('Epoch:','%04d' % epoch,
'D loss: {:.4}'.format(loss_val_D),
'G loss: {:.4}'.format(loss_val_G))
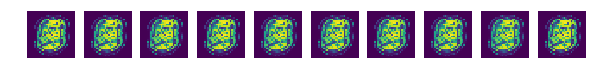
# You create and save images to check step of training
if epoch == 0 or (epoch + 1) % 10 == 0:
sample_size=10
noise=get_noise(sample_size,n_noise)
samples=sess.run(G,feed_dict={Z: noise})
fig,ax=plt.subplots(1,sample_size,figsize=(sample_size,1))
for i in range(sample_size):
ax[i].set_axis_off()
ax[i].imshow(np.reshape(samples[i],(28,28)))
plt.savefig('samples/{}.png'.format(str(epoch).zfill(3)),bbox_inches='tight')
plt.show()
plt.close(fig)
print('Finished optimization')
# < Epoch: 0000 D loss: -0.5567 G loss: -2.018
# < Epoch: 0001 D loss: -0.1307 G loss: -3.152
# < Epoch: 0002 D loss: -0.1392 G loss: -2.971
# < Epoch: 0003 D loss: -0.4306 G loss: -1.741
# < Epoch: 0004 D loss: -0.3265 G loss: -2.457
# < Epoch: 0005 D loss: -0.3006 G loss: -2.481
# < Epoch: 0006 D loss: -0.5117 G loss: -1.872
# < Epoch: 0007 D loss: -0.3749 G loss: -1.99
# < Epoch: 0008 D loss: -0.2547 G loss: -2.598
# < Epoch: 0009 D loss: -0.3928 G loss: -2.186
img cbd7fada-ec40-459c-a0a0-2026e870a1bb
 img 0ab553d1-c358-4d47-a952-4761ee3a6d0b
img 0ab553d1-c358-4d47-a952-4761ee3a6d0b


