007_lec_DQN.html
# https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=S1Y9eys2bdg&list=PLlMkM4tgfjnKsCWav-Z2F-MMFRx-2gMGG&index=14
# @
# In previous lectures, you used Q table algorithm,
# which works well in simple way
# But since it uses table structure,
# it can't solve big and complex problem
# @
# So, you tried not to express values in q table,
# but to express and approximate values by using q network
# You input "state" data into network,
# and network outputs reward data (predicted q values) for all actions
# @
# $$$\hat{Q}$$$ approximates to Q
# $$$\hat{Q}$$$ converges when you use Q table
# However, $$$\hat{Q}$$$ diverges when you use Q network due to 2 reasons,
# resulting in not efficient training by q network
# 1. Correlations between samples
# 1. Non-stationary targets
# @
# Above 2 issues were resolved by deepmind from DQN algorithms(2013, 2015)
# @
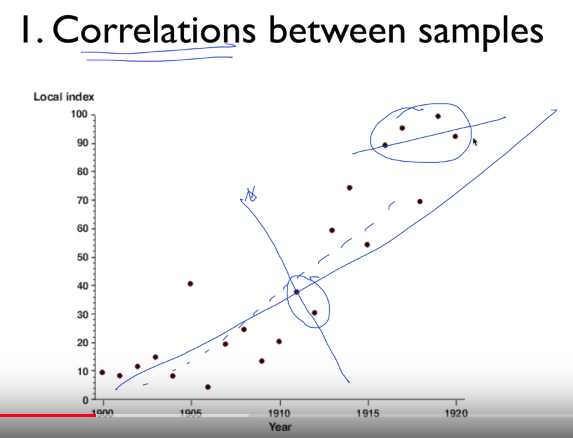
# Issue 1. Correlations between samples
# With 2 samples strongly correlated to each other
# With 4 samples strongly correlated to each other
# They can create different lines compared to target line
# img 2018-04-29 11-37-10.png
#  # @
# Issue 2. Non-stationary targets (moving target)
# y label (target) = $$$r_{t}+\gamma max_{a'} \hat{Q}(s_{t+1},a'|\theta)$$$
# prediction of Q or $$$\hat{y} = \hat{Q}(s_{t},a_{t}|\theta)$$$
# You should make them (target y, prediction Q) almost same
# For this, you should make prediction Q near to target y
# In other words, you update network (update parameter $$$\theta$$$),
# for $$$Q = \hat{Q}(s_{t},a_{t}|\theta)$$$
# But in this case, You should know above 2 terms (target y, prediction Q),
# runing in same network with same parameter $$$\theta$$$
# With this condition, automatically and inevitably,
# target y = $$$r_{t}+\gamma max_{a'} \hat{Q}(s_{t+1},a'|\theta)$$$ becomes to move by moved $$$\hat{y}$$$
# because they use same network and same parameter $$$\theta$$$
# In summary, changing parameter in prediction Q network leads to moving target y
# @
# DQN's three solutions for above issues
# 1. Go deep to refrect various state
# (multiple layers = convolution layers + pooling layers + fully connected layers + ...)
# 1. Captrue and replay ("experience replay" way)
# for "correlation between samples" issue
# You perform loop with giving "action",
# and you obtain "state"
# At this moment, you don't start training,
# but you store values (state,action,reward,...) into buffer
# After enough time, you extract values randomly,
# and start training with them
# 1. Separate networks: in other words, you create a target network
# for "non-stationary target" issue
# @
# It's bad idea to train with samples having strong correlations
# You can use "experience replay" to resolve this issue
# You iterate following steps, obtain "action", from "action" obtain "state"
# At this time of iteration, don't train (weights), but store actions and states into buffter
# Then, you extract several values randomly from buffer
# You train model with them
# img 2018-04-29 12-35-17.png
#
# @
# Issue 2. Non-stationary targets (moving target)
# y label (target) = $$$r_{t}+\gamma max_{a'} \hat{Q}(s_{t+1},a'|\theta)$$$
# prediction of Q or $$$\hat{y} = \hat{Q}(s_{t},a_{t}|\theta)$$$
# You should make them (target y, prediction Q) almost same
# For this, you should make prediction Q near to target y
# In other words, you update network (update parameter $$$\theta$$$),
# for $$$Q = \hat{Q}(s_{t},a_{t}|\theta)$$$
# But in this case, You should know above 2 terms (target y, prediction Q),
# runing in same network with same parameter $$$\theta$$$
# With this condition, automatically and inevitably,
# target y = $$$r_{t}+\gamma max_{a'} \hat{Q}(s_{t+1},a'|\theta)$$$ becomes to move by moved $$$\hat{y}$$$
# because they use same network and same parameter $$$\theta$$$
# In summary, changing parameter in prediction Q network leads to moving target y
# @
# DQN's three solutions for above issues
# 1. Go deep to refrect various state
# (multiple layers = convolution layers + pooling layers + fully connected layers + ...)
# 1. Captrue and replay ("experience replay" way)
# for "correlation between samples" issue
# You perform loop with giving "action",
# and you obtain "state"
# At this moment, you don't start training,
# but you store values (state,action,reward,...) into buffer
# After enough time, you extract values randomly,
# and start training with them
# 1. Separate networks: in other words, you create a target network
# for "non-stationary target" issue
# @
# It's bad idea to train with samples having strong correlations
# You can use "experience replay" to resolve this issue
# You iterate following steps, obtain "action", from "action" obtain "state"
# At this time of iteration, don't train (weights), but store actions and states into buffter
# Then, you extract several values randomly from buffer
# You train model with them
# img 2018-04-29 12-35-17.png
#  # @
# You store actions, rewards, states into buffer D
# You extract samples randomly from buffer D,
# and you create mini batch with them,
# and you train model with those batches
# img 2018-04-29 12-37-43.png
#
# @
# You store actions, rewards, states into buffer D
# You extract samples randomly from buffer D,
# and you create mini batch with them,
# and you train model with those batches
# img 2018-04-29 12-37-43.png
#  # @
# Why does above technique work?
# Key is "you extract sample randomly",
# which can reflect distribution of entire data,
# with avoiding extracting strongly correlated samples
# img 2018-04-29 12-40-11.png
#
# @
# Why does above technique work?
# Key is "you extract sample randomly",
# which can reflect distribution of entire data,
# with avoiding extracting strongly correlated samples
# img 2018-04-29 12-40-11.png
#  # @
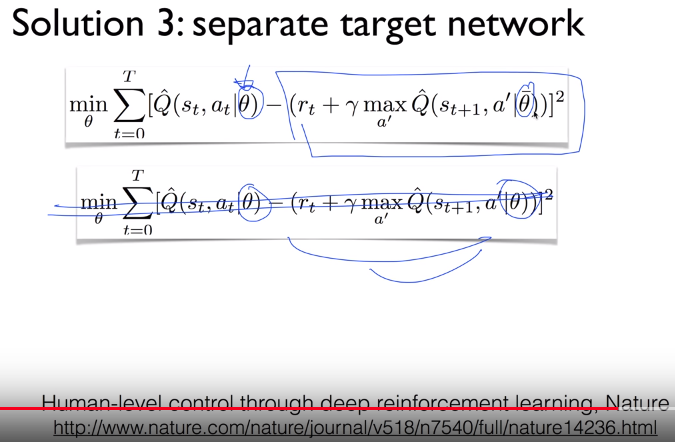
# You will use two separated parameters $$$\theta$$$ and $$$\bar{\theta}$$$,
# which means you use separated different network for y and $$$\hat{y}$$$
# You won't use second formular in following illustration,
# which has only one $$$\theta$$$ for both y and $$$\hat{y}$$$
# Step:
# You bring label y from second term,
# and you stay it,
# and you update first term
# img 2018-04-29 12-45-50.png
#
# @
# You will use two separated parameters $$$\theta$$$ and $$$\bar{\theta}$$$,
# which means you use separated different network for y and $$$\hat{y}$$$
# You won't use second formular in following illustration,
# which has only one $$$\theta$$$ for both y and $$$\hat{y}$$$
# Step:
# You bring label y from second term,
# and you stay it,
# and you update first term
# img 2018-04-29 12-45-50.png
#  # img 2018-04-29 12-46-42.png
#
# img 2018-04-29 12-46-42.png
# 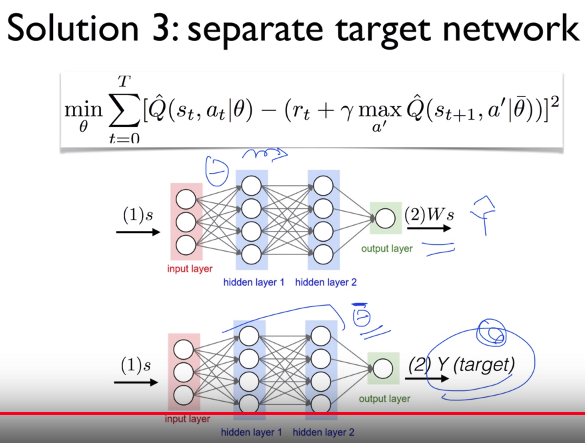 # You copy parameters from first network into second network
# In formular in box,
# $$$r_{j}+\gamma max_{a'} \hat{Q}(\phi_{j+1},a';\bar{\theta})$$$ is target $$$y_{j}$$$,
# you will create target from $$$\bar{\theta}$$$
# You will create prediction from another network using $$$\theta$$$
# $$$Q(\phi_{j},a_{j};\theta)$$$
# And you will perform gradient descent in respect to $$$\theta$$$,
# which means you update only second main network,
# without touching target network $$$y_{j}$$$ having $$$\bar{\theta}$$$
# And then, after enough time, you copy Q into $$$\hat{Q}$$$
# img 2018-04-29 12-53-19.png
#
# You copy parameters from first network into second network
# In formular in box,
# $$$r_{j}+\gamma max_{a'} \hat{Q}(\phi_{j+1},a';\bar{\theta})$$$ is target $$$y_{j}$$$,
# you will create target from $$$\bar{\theta}$$$
# You will create prediction from another network using $$$\theta$$$
# $$$Q(\phi_{j},a_{j};\theta)$$$
# And you will perform gradient descent in respect to $$$\theta$$$,
# which means you update only second main network,
# without touching target network $$$y_{j}$$$ having $$$\bar{\theta}$$$
# And then, after enough time, you copy Q into $$$\hat{Q}$$$
# img 2018-04-29 12-53-19.png
# 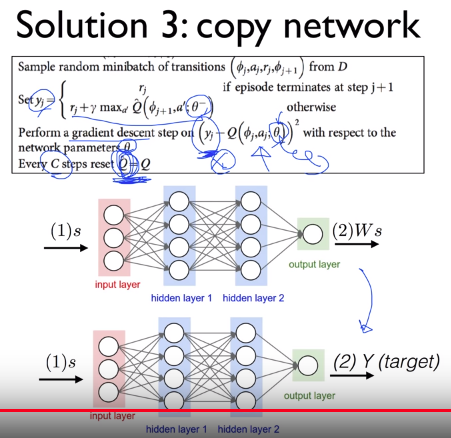 # @
# Understanding Nature Thesis Paper(2015) about DQN
# 1. You create replay memory buffer named D
# 1. You create Q main network and $$$\bar{Q}$$$ target network
# At initial time, you make those two network same, $$$\bar{\theta}=\theta$$$
# 1. You select action,
# you can select action randomly or by using Q network
# You execute "action",
# You get values like reward, state,
# And then, don't train network but copy values into buffer D
# ...
# img 2018-04-29 12-59-03.png
#
# @
# Understanding Nature Thesis Paper(2015) about DQN
# 1. You create replay memory buffer named D
# 1. You create Q main network and $$$\bar{Q}$$$ target network
# At initial time, you make those two network same, $$$\bar{\theta}=\theta$$$
# 1. You select action,
# you can select action randomly or by using Q network
# You execute "action",
# You get values like reward, state,
# And then, don't train network but copy values into buffer D
# ...
# img 2018-04-29 12-59-03.png
# 







